Product Info Summary
| SKU: | A00277-1 |
|---|---|
| Size: | 80 µl |
| Reactive Species: | Human |
| Host: | Rabbit |
| Application: | Flow Cytometry, IF, IHC-P, WB |
Customers Who Bought This Also Bought
Product info
Product Name
Anti-CHEK2 Antibody (N-term)
SKU/Catalog Number
A00277-1
Size
80 µl
Form
Liquid
Description
Boster Bio Anti-CHEK2 Antibody (N-term) (Catalog # A00277-1). Tested in WB, IF, Flow Cytometry, IHC-P application(s). This antibody reacts with Human.
Storage & Handling
Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long-term storage, store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles.
Cite This Product
Anti-CHEK2 Antibody (N-term) (Boster Biological Technology, Pleasanton CA, USA, Catalog # A00277-1)
Host
Rabbit
Contents
Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide.
Clonality
Polyclonal
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
Immunogen
This CHEK2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 111-141 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CHEK2.
*Blocking peptide can be purchased. Costs vary based on immunogen length. Contact us for pricing.
Cross-reactivity
No cross reactivity with other proteins.
Reactive Species
A00277-1 is reactive to CHEK2 in Human
Applications
A00277-1 is guaranteed for Flow Cytometry, IF, IHC-P, WB Boster Guarantee
Observed Molecular Weight
Calculated molecular weight
60915 Da
Background of Chk2
CHEK2 is a cell cycle checkpoint regulator and putative tumor suppressor. It contains a forkhead-associated protein interaction domain essential for activation in response to DNA damage and is rapidly phosphorylated in response to replication blocks and DNA damage. When activated, the encoded protein is known to inhibit CDC25C phosphatase, preventing entry into mitosis, and has been shown to stabilize the tumor suppressor protein p53, leading to cell cycle arrest in G1. In addition, this protein interacts with and phosphorylates BRCA1, allowing BRCA1 to restore survival after DNA damage. Mutations in this gene have been linked with Li-Fraumeni syndrome, a highly penetrant familial cancer phenotype usually associated with inherited mutations in TP53.
Antibody Validation
Boster validates all antibodies on WB, IHC, ICC, Immunofluorescence, and ELISA with known positive control and negative samples to ensure specificity and high affinity, including thorough antibody incubations.
Assay dilution & Images
Assay Dilutions Recommendation
The recommendations below provide a starting point for assay optimization. The actual working concentration varies and should be decided by the user.
IF: 1:10-1:50
WB: 1:1000
IHC-P: 1:50-1:100
FC: 1:10-1:50
Validation Images & Assay Conditions

Click image to see more details
Confocal immunofluorescent analysis of CHEK2 Antibody (N-term) with HepG2 cell followed by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit lgG (green).Actin filaments have been labeled with Alexa Fluor 555 phalloidin (red).DAPI was used to stain the cell nuclear (blue).

Click image to see more details
CHEK2 Antibody (N-term) western blot analysis in K562,NCI-H460 cell line lysates (35ug/lane).This demonstrates the CHEK2 antibody detected the CHEK2 protein (arrow).

Click image to see more details
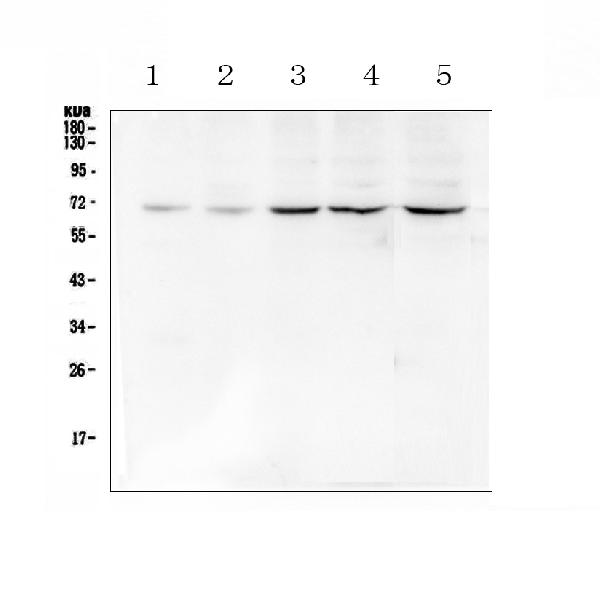
All lanes : Anti-CHEK2 Antibody (N-term) at 1:1000 dilution
Lane 1: HCT116 whole cell lysate
Lane 2: Jurkat whole cell lysate
Lysates/proteins at 20 µg per lane.
Secondary
Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG, (H+L), Peroxidase conjugated at 1/10000 dilution.
Predicted band size : 61 kDa
Blocking/Dilution buffer: 5% NFDM/TBST.

Click image to see more details
CHEK2 Antibody (N-term) IHC analysis in formalin fixed and paraffin embedded colon carcinoma followed by peroxidase conjugation of the secondary antibody and DAB staining. This data demonstrates the use of the CHEK2 Antibody (N-term) for immunohistochemistry. Clinical relevance has not been evaluated.

Click image to see more details
CHEK2 Antibody (N-term) flow cytometric analysis of K562 cells (right histogram) compared to a negative control cell (left histogram).FITC-conjugated goat-anti-rabbit secondary antibodies were used for the analysis.
Protein Target Info & Infographic
Gene/Protein Information For CHEK2 (Source: Uniprot.org, NCBI)
Gene Name
CHEK2
Full Name
Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk2
Weight
60915 Da
Superfamily
protein kinase superfamily
Alternative Names
CDS1; CHEK2; CHK2 checkpoint homolog (S. pombe); Chk2; EC 2.7.11; EC 2.7.11.1; HuCds1; LFS2; PP1425; Rad53; S.pombe) homolog CHEK2 CDS1, CHK2, HuCds1, LFS2, PP1425, RAD53, hCds1 checkpoint kinase 2 serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk2|CHK2 checkpoint homolog|cds1 homolog|checkpoint-like protein CHK2
*If product is indicated to react with multiple species, protein info is based on the gene entry specified above in "Species".For more info on CHEK2, check out the CHEK2 Infographic

We have 30,000+ of these available, one for each gene! Check them out.
In this infographic, you will see the following information for CHEK2: database IDs, superfamily, protein function, synonyms, molecular weight, chromosomal locations, tissues of expression, subcellular locations, post-translational modifications, and related diseases, research areas & pathways. If you want to see more information included, or would like to contribute to it and be acknowledged, please contact [email protected].
Specific Publications For Anti-CHEK2 Antibody (N-term) (A00277-1)
Hello CJ!
No publications found for A00277-1
*Do you have publications using this product? Share with us and receive a reward. Ask us for more details.
Recommended Resources
Here are featured tools and databases that you might find useful.
- Boster's Pathways Library
- Protein Databases
- Bioscience Research Protocol Resources
- Data Processing & Analysis Software
- Photo Editing Software
- Scientific Literature Resources
- Research Paper Management Tools
- Molecular Biology Software
- Primer Design Tools
- Bioinformatics Tools
- Phylogenetic Tree Analysis
Customer Reviews
Have you used Anti-CHEK2 Antibody (N-term)?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
- $30 for a review with an image
0 Reviews For Anti-CHEK2 Antibody (N-term)
Customer Q&As
Have a question?
Find answers in Q&As, reviews.
Can't find your answer?
Submit your question