This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
- Table of Contents
Need your GOI packaged into AAV? Our innovative AAV production service produces up to 1E+13GC/mL AAV in one single production. Get a free consultation today and take advantage of our easy to work with AAV packaging expertise.
How much does aav cost?
Our standard AAV packaging services pricing are listed in the table below.
| Titer | Volume | Lead time | DNA required | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10^11 GC/mL, Crude | 300 µL | 2-3 weeks | 75 μg | $520 |
| 10^12 GC/mL, Purified | 1 mL | 3-4 weeks | 400 μg | $1,200 |
| 10^13 GC/ml, Purified | 200 µL | 3-4 weeks | 750 μg | $1,750 |
| 10^13 GC/ml, Purified | 400 µL | 3-4 weeks | 750 μg | $2,400 |
| 10^13 GC/ml, Purified | 1 mL | 3-4 weeks | 750 μg | $3,600 |
*The price is for AAV packaging only and does not include GOI cloning in to AAV package-ready vector, or DNA amplifcation.
Begin inquiryAt Boster Bio, we offer high quality AAVs with low capsids vacancy that maximize infection efficiency for all tissue types. Our AAV packaging is fast and competitively priced.
We can cover the entire viral portion of your project, from gene synthesis, cloning to vector construction and packaging and anything else in between.
Our AAVs are Research Grade Only for use in the early stages of drug discovery R&D to test your Gene of Interest in vitro or with in vivo animal studies.
Ideal for research and pharma clients to outsource partial or total AAV production.
Gene Synthesis
Clone Gene into the Vector
Packaging into viral vector and expanding
Quality Control
As easy as 1, 2, 3.
Boster Bio can offer two different AAV production systems tailored to your needs. We can accommodate for your gene of interest of up to 4.7kb in size
Utilizing a unique packaging mix for each different serotype, our triple transfection AAV system in HEK293 cells contain two plasmids which separate the AAV structural and replication genes until the time of viral production. This prevents the structural genes from being present in the genome of the produced virus, and increases the safety of the user by making the viruses replication incompetent.
If you are looking for a custom order involving a non-standard volume, titer, purification or require a fast turnaround or delivery, please get in contact to discuss further.
Our expert team are on hand to discuss your project further and provide accurate details in regards to pricing and estimated delivery times.
Want to know more about these cool technologies or license it? Contact us today.
High
efficiency
High Purity
high Potency
Guaranteed
titer
Proprietary
technologies
Serving Science
since 1993



We guarantee titer and end applications:
AAV's Transduction Efficiency depends capsid-receptor interaction, cellular uptake and translation. 3 key factors affect AAV transduction success: correct serotype to tissue match, high titer of capsids and high percentage of effective capsids.
Recombinant AAV (rAAV) delivers targeted specificity and low immunogenicity. Therefore it is a powerful tool for in vivo gene delivery, and as a result AAV has become the dominant form of gene therapy for genetic diseases. AAV used in the only two FDA-approved gene therapies currently available and is driving many of today’s therapeutic discoveries.
Most gene therapy vectors work by integrating their genetic material into a patient’s cells; however, rAAV-delivered genes remain in the extrachromosomal state and are not incorporated into the host genome. This is an advantage, as rAAV vectors can infect both quiescent and dividing cells and are not known to cause diseases in humans.
AAV is the most promising candidate for virus-based gene therapy as it:
In gene and cell therapeutics, the need for producing high concentrations or titers of AAV is driven by its ability to infect a cell. While an individual AAV’s ability to infect a cell is dependent on its capsid construction and the cell it is infecting, it’s efficiency can also be titer dependent. An AAV particle needs to be in contact with the cell surface in order to infect it, so in order to ensure a better infection rate we may need to increase the AAV concentration.
However not all titers are the same. The physical titer is the concentration of viral particles containing viral genomes but this may differ to the infectious titer which is the concentration of viral particles that can transduce cells. So the ratio of physical to infectious viral particles indicates the specific infectivity of AAV preparations. A further consideration also needs to be made for the ratio of full to empty capsids as the amount of genome-containing viral particles compared to the total number of capsids.
If a high level of gene expression is required, then a higher titer of AAV may need to be produced. For example, fluorescent proteins may require many viral particles to infect a cell to show visible expression of the protein.
As many AAV particles are required in order to infect a cell to produce expression, in most cases the higher the titer the better.
Differences between cell surface receptors of the AAV serotype determine its tropism but it is also believed to be affected by cellular uptake, intracellular processing, nuclear delivery of the vector genome, uncoating, and second strand DNA synthesis. After discovering that the capsid surface proteins can determine the tropism, scientists have genetically modified the viral capsid, and generated mosaic vectors to create chimeric virions by swapping domains or amino-acids between serotypes. This has allowed researchers to specifically target cells with certain serotypes to effectively transduce and express genes in a localized area. To date, a total of 11 serotypes of AAV have been described and each with its own unique traits and tropisms.
| Serotype | Tissue Tropism |
|---|---|
| AAV1 | Smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, CNS, brain, lung, retina, inner ear, pancreas, heart, liver |
| AAV2 | Smooth muscle, CNS, brain, liver, pancreas, kidney, retina, inner ear, testes |
| AAV2.7m8 | Retina, inner ear |
| AAV2-retro | Spinal nerves |
| AAV3 | Smooth muscle, liver, lung |
| AAV4 | CNS, retina, lung, kidney, heart |
| AAV5 | Smooth muscle, CNS, brain, lung, retina, heart, immune system |
| AAV6 | Smooth muscle, heart, lung, pancreas, adipose, liver, immune system |
| AAV7 | Smooth muscle, retina, CNS, brain, liver |
| AAV8 | Smooth muscle, CNS, brain, retina, inner ear, liver, pancreas, heart, kidney, adipose |
| AAV9 | Smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, lung, liver, heart, pancreas, CNS, retina, inner ear, testes, kidney, adipose |
| AAVShH10 | Retina |
| AAVrh10 | Retina, liver, brain |
| AAV-DJ | Liver, heart, kidney, spleen, retina |
| AAV-PHP.eB | CNS |
| AAV10 | Kidney, Uterus, heart, liver, lung, skeletal muscle |
| AAV11 | Kidney, spleen, stomach, heart, lung skeletal muscle |
| Tissue Type | Recommended AAV Serotype |
|---|---|
| Smooth Muscle | AAV1, AAV2, AAV3, AAV5, AAV6, AAV7, AAV8, AAV9 |
| Skeletal Muscle | AAV1, AAV9, AAV10, AAV11 |
| CNS | AAV1, AAV2, AAV4, AAV5, AAV7, AAV8, AAV9, AAV-PHP.eB |
| Brain | AAV1, AAV2, AAV5, AAV7, AAV8 |
| Retina | AAV1, AAV2, AAV2.7m8, AAV4, AAV5, AAV7, AAV8, AAV9, AAVShH10, AAVrh10, AAV-DJ |
| Inner Ear | AAV1, AAV2, AAV6.2, AAV8, AAV9, AAV2.7m8 |
| Lung | AAV1, AAV3, AAV4, AAV5, AAV6, AAV6.2, AAV9, AAV10, AAV11 |
| Liver | AAV1, AAV2, AAV3, AAV6, AAV6.2, AAV7, AAV8, AAV9, AAVrh10, AAV-DJ, AAV10 |
| Pancreas | AAV1, AAV2, AAV6, AAV8, AAV9 |
| Heart | AAV1, AAV4, AAV5, AAV6, AAV8, AAV9, AAV-DJ, AAV10, AAV11 |
| Kidney | AAV2, AAV4, AAV8, AAV9, AAV-DJ, AAV10, AAV11 |
| Adipose | AAV6, AAV8, AAV9 |
| Testes | AAV2, AAV9 |
| Spleen | AAV-DJ, AAV11 |
| Spinal Nerves | AAV2-retro |
We can also offer other serotypes not listed above. Please contact us for more information
Contact Us
Left: EGFP expression (Green) in lumbar neuronal cells 4 weeks after intrathecal injection of AAV-EGFP Serotype 9 (Cat. # iAAV01509) into mice.
Right: Overlay with β-tubulin (red) and DAPI (blue).
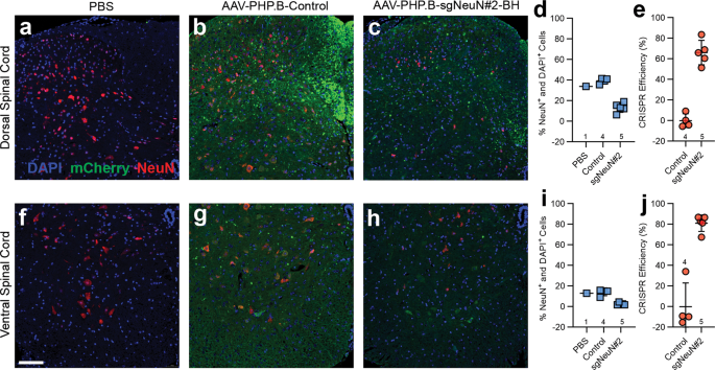
Immunohistochemical staining reveals robust NeuN gene disruption in the spinal cord.
Still got questions about our AAV packaging services?
Q1. What AAV Volumes Do You Offer?
Q2. What Is Your Expected Turnaround Time?
Q3. How Do I Choose The Right AAV Packaging Service For My Needs?
Q4. What Experiments Can I Perform With AAVs?
Q6. What disadvantages are there in using AAV?
Q7. Is high yield or high purity of more importance?
In general, the titer is of more importance because it is a measurement of the number of viral particles per volume.
Purity will be a more important consideration for in vivo studies. If the virus is not pure, it could cause undesired responses to the experimental animals. Our high titer AAVs are suitable for in vivo studies.
For more information on why AAV titer is important click here.
Q8. Is the small cellular immune response going to be an issue?
Q9. Storage, ordering and shipping
Our storage solution for AAVs produced via triple transfection is PBS with 5% Glycerol, which is suitable for in vivo injection. For AAV’s produced using the Baculovirus system storage solution is 1xPBS buffer containing 0.001% pluronic F-68. AAV is stable at 4° C for short-term use and room temperature for immediate use. For long-term storage, AAV should be stored at -80° C for best quality and longevity. Although AAV is a very stable virus, multiple freeze-thaw cycles may reduce the titer of the product.
For Shipping, Ordering and Storage details please see our Sample Collection Guidelines.
Q10. What size does the gene of interest need to be?
Q11. What are the AAV 5.2 and AAV 8.2 products?
Q12. How do I order pre-made controls?
Q13. How far in advance do you have to schedule an AAV Production project?
Q14. Can you make the AAV without any plasmid?
Q15. What do I need to send to Boster Bio?
Initially we will need to know the following in order to send you a quote:
Please contact our Project Concierge to discuss your specific requirements and we will tailor the service to your needs.
If you accept the quote and wish to proceed with one of Boster’s AAV Packaging Services, we require the following materials:
Q16. What is the expected yield for AAV production?
We use vector genome (vg) as our unit to measure AAV production scale. This unit is similar to genome copy (gc) – it refers to the number of complete copies of the gene of interest that are present in the final suspension.
The titer (in vg/mL), or concentration, of our virus products is typically ~2 x 10^13 vg/mL. However, some genes are either toxic to cells or detrimental to AAV efficiency, and some serotypes (e.g, AAV 2, 3, 6) are low yield. In these cases, the expected titer may be lower.
Both titer and volume can be adjusted to the customer’s requirements, but the price of the product will always depend on the vector genome (vg) amount.
For more details on expected yields for your specific project, contact the Project Concierge.
Q17. What type of QC do you have for each AAV stock?
Our QC details can be found here and are detailed below: