This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
- Table of Contents

Dilution ratio describes a simple dilution – a unit volume of solute (or sample) is combined with a desired unit volume of solvent (or diluent), to reach a desired total volume (Vsolute + Vsolvent = Total Vsolution)
Thus, a dilution ratio of 1:4 describes 1 part solute + 4 parts solvent = 5 parts total. The sum of both solute plus solvent equals total, final volume.
Boster Bio offers an in-depth ELISA data analysis guide:
Serial dilutions are a series of dilutions prepared using the same dilution factor – often performed to use as standard concentrations (or quantities) for quantification assays. Using the same dilution factor over a series of dilutions results in a logarithmic decrease in solute concentration across the series. The standard concentrations are used to create a calibration, or standard curve spanning the linearity range of an assay. The target concentration or amount may then be calculated from this curve.
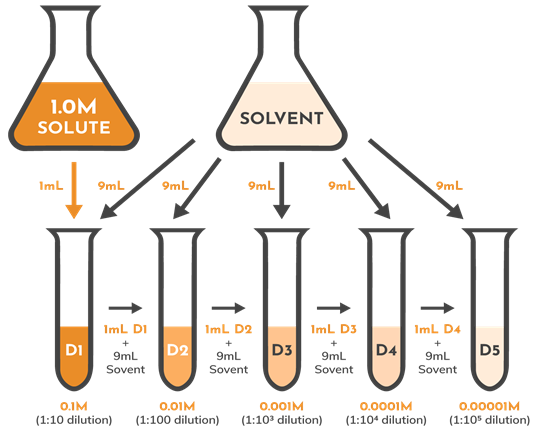
Here’s what a tenfold serial dilution looks like
Need a little help with your calculations?
Click on the image below for calculators for everything from simple dilutions to complex serial dilutions.
Dilution factor describes the ratio of the initial volume of solute to the total volume of the diluted solution (Vsolute x Vsolvent = Total Vsolution). Dilution factors are of particular importance when performing serial dilutions.
Thus, a dilution factor of 1:4 describes 1 part solute dissolved in 4 parts solvent = 4 total parts. The product of solute times solvent equals total, final volume.
The ambiguity between the two terms derives from the convention of presenting both as a ratio. In other words, asking different people to perform a 1 to 2 dilution will get varying results over requesting to dilute a sample in half. Both are commonly expressed in writing and textbooks though as 1:2. In strictest terms, a dilution is expressed as parts over parts to differentiate, ½ in this example, or as an exponent.