This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
- Table of Contents
Learn about the health benefits of various vitamins from this colorful infographic and check out available vitamin detection kits from Boster!
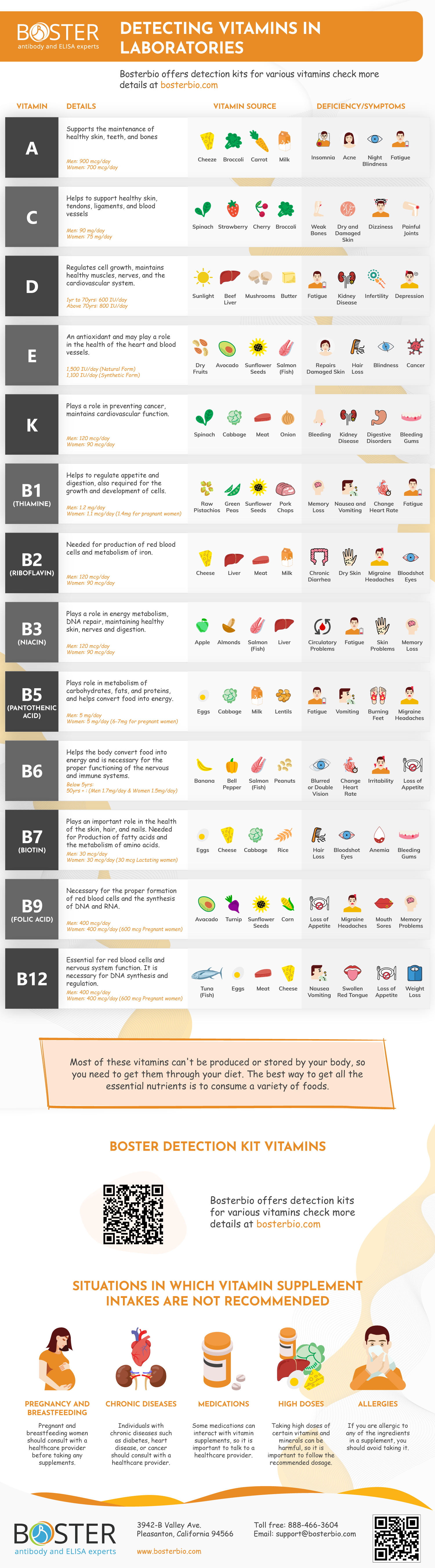
There are thirteen essential vitamins that the human body requires to function properly. These vitamins are Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Vitamin K, Vitamin B1 (Thiamine), Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (Niacin), Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid), Vitamin B6, Vitamin B7 (Biotin), Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid), and Vitamin B12.
Vitamin A plays a role in vision, the immune system, and cell growth. It also supports the maintenance of healthy skin, teeth, and bones. It plays a role in cell growth and differentiation and helps regulate the immune system. A deficiency in vitamin A can lead to night blindness, dry eyes, and a weakened immune system, among other health problems A variety of foods contain it, including sweet potatoes, carrots, and leafy greens. It can also be found in animal-derived foods such as liver, milk, eggs.
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid is an antioxidant and is important for the production of collagen, a protein that helps to support healthy skin, tendons, ligaments, and blood vessels. It helps in the absorption of iron from plant-based foods, the healing of wounds, and the maintenance of healthy bones. Among the fruits and vegetables that contain it are oranges, strawberries, and kiwis.
Vitamin D is essential in maintaining overall health. It is best known for its role in calcium metabolism, helping the body absorb and use calcium to maintain strong bones and teeth. Adequate Vitamin D intake helps to prevent osteoporosis and rickets. Vitamin D also plays a role in the immune system, helping to fight off infections and inflammatory diseases. It also plays a role in the regulation of cell growth and in the maintenance of healthy muscles, nerves, and the cardiovascular system. Vitamin D can be obtained from the diet in small amounts, but the majority is produced by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight, specifically ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation. People who live in northern latitudes or who spend most of their time indoors are at a higher risk of vitamin D deficiency. Moreover, certain groups such as older adults, dark-skinned individuals, and people with fat malabsorption disorders may have a harder time getting enough Vitamin D from sunlight.
Vitamin E is an antioxidant and may play a role in the health of the heart and blood vessels. It helps to neutralise harmful free radicals which can damage cells and contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease. Additionally, vitamin E is important for maintaining the integrity of cell membranes, which helps to protect cells from damage and infection. It can be found in nuts and seeds, as well as in leafy green vegetables.
Vitamin K plays a role in blood clotting and maintaining healthy bones. Additionally, it has been found to be important for maintaining healthy cardiovascular function, as it helps to regulate the balance of calcium in the body. It also has been suggested that it plays a role in preventing cancer. It can be found in leafy green vegetables, such as broccoli and spinach. Vitamin K deficiency can cause excessive bleeding, easy bruising and anaemia.
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) is important for the metabolism of carbohydrates and the proper function of the nervous system. It helps to convert carbohydrates into energy and is necessary for the metabolism of sugars and starches. Additionally, it helps to regulate appetite and digestion and is required for the normal growth and development of cells. It can be found in whole grains, nuts, and seeds. A deficiency of Vitamin B1 can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, muscle weakness, and irritability, and can also cause serious neurological disorders such as Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in energy metabolism and the maintenance of healthy skin, eyes, and nerves. It is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, and helps to convert food into energy. Vitamin B2 is also needed for the production of red blood cells and for the metabolism of iron, which is important for maintaining healthy blood. Vitamin B2 can be found in a variety of foods including dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals. A deficiency of Vitamin B2 can cause symptoms such as sore throat, cracks and sores in the corners of the mouth, skin rashes, and fatigue.
Vitamin B3 (Niacin) is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in energy metabolism, DNA repair, and maintaining healthy skin, nerves and digestion. It is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins, and helps to convert food into energy. It can be found in a variety of foods including meats, fish, and fortified cereals. A deficiency of Vitamin B3 can cause symptoms such as skin rashes, indigestion, and fatigue. Severe deficiency can lead to a condition called pellagra which causes inflammation of the skin, digestive issues and neurological disorders.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) plays a crucial role in energy metabolism and the synthesis of various important compounds in the body. It is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, and helps to convert food into energy. Among the foods that contain it are meats, whole grains, and leafy greens. A deficiency of Vitamin B5 is rare, but when it occurs, it can cause symptoms such as fatigue, irritability, and numbness in the hands and feet. Adequate intake of Vitamin B5 is essential to support the body's energy metabolism and the synthesis of important compounds.
For the formation of red blood cells and the proper functioning of the immune and nervous systems, vitamin B6 is essential. It helps the body convert food into energy and is necessary for the proper functioning of the nervous and immune systems. It also helps the body make haemoglobin, which is the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body's tissues. It can be found in foods such as fish, poultry, and leafy green vegetables. Deficiency in vitamin B6 can lead to anaemia, skin disorders, and nervous system disorders.
Among its many functions, vitamin B7 (Biotin) plays a fundamental role in the metabolic process of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It helps the body convert food into energy. Biotin also plays an important role in the health of the skin, hair, and nails, and it is necessary for the production of fatty acids and the metabolism of amino acids. It can be found in eggs, dairy products, and nuts. A deficiency in vitamin B7 can lead to skin rash, hair loss, and anaemia.
Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid) is essential for red blood cell production and nervous system development. is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in many of the body's metabolic processes. It is necessary for the proper formation of red blood cells and the synthesis of DNA and RNA. Folate is also essential for the proper growth and development of the nervous system, particularly in infants and fetuses. Adequate intake of folate is especially important for women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, as deficiency in vitamin B9 has been linked to neural tube defects in developing fetuses. It can be found in leafy green vegetables, as well as in fruits such as oranges and melons. A deficiency in vitamin B9 can lead to anemia, birth defects and cognitive disorders.
In order to form red blood cells and maintain proper nervous system function, Vitamin B12 is essential. Vitamin B12 is also involved in the metabolism of every cell in the body and is necessary for DNA synthesis and regulation. It can be found in animal-derived foods such as meats, fish, and dairy products. Deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to anemia, nerve damage, and cognitive impairment. People who are at risk for deficiency include vegetarians and vegans, people with pernicious anemia, and older adults.
Most of these vitamins can't be produced or stored by your body, so you need to get them through your diet. The best way to get all the essential nutrients is to consume a variety of foods. Deficit diseases can occur if these vitamins are insufficiently consumed while an excess intake of some vitamins can also lead to health problems. It is also important to pay attention to portion sizes and limit processed foods, added sugars, and saturated fats.
There are certain situations in which it is not recommended to take vitamin supplements. These include:
It is always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any vitamin or mineral supplement, especially if you have any health conditions, or if you are taking any medications. This will ensure that the supplement is safe for you to take and that it will not interact with any other medications or treatments that you are currently receiving.
Check out our vitamin detection kits!